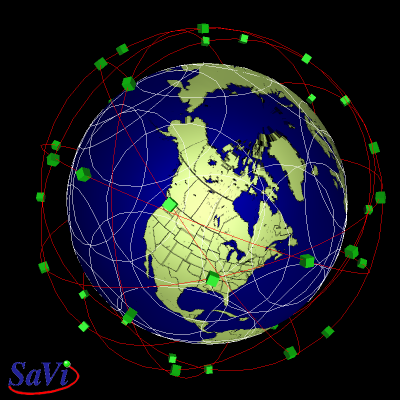
Full active Globalstar constellation as modelled in SaVi
Here is the official
Globalstar website. (Globalstar also appear to have a restricted-access website).
Other Globalstar sites include:
The failure to launch twelve satellites on a Zenit-2
in September 1998 was reduced from streaming video to a single line in their now-vanished
launch schedule, although a press release
concerning the launch failure was later put up.
After that disaster they made a public satellite phone call to demonstrate that what was already up is
functional. Later launches did not use Zenits.
Globalstar coverage is limited to regions that lie within the same satellite footprint
as a gateway station, and Globalstar associates have built far fewer gateway stations
than originally planned. Although the rosette constellation geometry allows
coverage between latitudes of +/- 68 degrees or so, you still need to be in
the footprint with a gateway station to complete a call. Coverage areas are limited, although they're now covering most of Alaska. Further information on coverage and roaming is available from Globalstar Canada.
Globalstar - it's not global, and it's not based on a Walker star geometry.
Thermo Capital Partners LLC has taken control of Globalstar. (Associated Press, 16 April 2004)
Here are the related Thermo-Globalstar FCC applications.
ICO Global made a bid for Globalstar. Here's a copy of the bid terms (16 April 2003) and the press release detailing the deal (28 April 2003). They withdrew their bid in October 2003.
Globalstar was in talks to be sold to Bennett LeBow's New Valley Corporation, but the deal collapsed thanks to a disagreement in terms.
Globalstar finally files for Chapter 11 US bankruptcy protection on
15 February 2002. This has been anticipated for some time.
Globalstar
lays off half its staff (August 2001)
Please don't ask me about finance-related matters. Please don't ask me about
pending class-action
lawsuits. A number of class-action lawsuits have been announced.
If you have a holding in Globalstar, take a look at
recent stock data. Here's idle financial discussion of Globalstar and Motley Fool discussion.
Globalstar officially launched their service at Geneva Telecom '99
on 13 October 1999. Their current country coverage has been increasing; the CIA World Factbook doesn't think that Bermuda, Gibraltar or Yugoslavia are countries...
The Globalstar Launch Information Line is +1-408-933-4000
The Boeing Delta Launch Information Line is +1-714-896-4770
Globalstar recently signed for several launches with Boeing and for
an Ariane launch. Interesting -
Ariane hasn't been utilised by US constellation companies.
Soyuz launches were delayed as the Russians and Americans played
political tit-for-tat over inspecting launches, but a tight launch schedule was announced
as soon as an agreement was signed in January 1999. There are quotas. (from Wired News, who couldn't
make up their minds about the details of the remaining launches.)
Globalstar status is described by the Satellite News Digest.
If you want to track the satellites using the two-line element set format, here's a recent
NORAD two-line
element set for Globalstar. They set up
an intermediate constellation of 8 planes of 5 satellites each before
moving to the final 8x6 configuration. Later, after satellite failures, Globalstar returned to a 40-satellite configuration. More details on that are provided in Globalstar's SEC filing of 31 March 2003.
There's a regularly-updated downloadable TLE set
from NORAD via NASA's OIG - log
into their archive to get historical information. Orbitessera (mirror) may also be useful.
Launch dates below should be local to the time at the launch site.
Globalstar announces successful second launch of six new satellites, Globalstar press release, 14 July 2011.
Six satellites from Baikonur.
First launch of second-generation satellites
Globalstar Announces Successful Launch of Six New Second-Generation Satellites, Globalstar press release, 20 Ocotober 2010.
Six satellites from Baikonur.
Fifteenth and sixteenth launches
Eight satellites in 2007.
Globalstar announces successful launch of four satellites, Oct 22 2007 press release. From Baikonur on Soyuz.
four satellites on Soyuz from Baikonur, May 2007.
Fourteenth launch
The four remaining Globalstar satellites (64 were built) were launched on 8 February 2000 as in-orbit spares on a Delta II. Launch coverage is provided by Florida Today Space Online, and here's the Boeing media kit. Coverage from Spaceflight Now includes Quicktime videos. Here are videos of satellite deployment.
Thirteenth launch
A Soyuz carrying four satellites launched on 22 November 1999.
Twelfth launch
A Soyuz carrying four satellites launched on 18 October 1999.
Eleventh launch
A Soyuz carrying four satellites launched on 22 September 1999.
Tenth launch
A Boeing Delta carrying four satellites launched on Tuesday 17 August 1999. Here's the Boeing media kit.
Ninth launch
A Boeing Delta carrying four satellites launched on Sunday 25 July 1999. Here's the Boeing media kit.
Eighth launch
A Boeing Delta carrying four satellites launched on Saturday 10 July 1999 after delays due to high winds. Here's the
Boeing media kit.
Seventh launch
Third Boeing Delta II carrying four satellites from Cape Canaveral,
launched on Thursday 10 June 1999 after delays due to bad weather. Here's the Boeing media kit.
Sixth launch
Four satellites on a Soyuz-Ikar from Baikonur launched on Wednesday April 14 1999.
I didn't notice this launch at the time - thanks to Perry Stout for pointing it out
after the fact.
Fifth launch
Four satellites on a Soyuz-Ikar from Baikonur launched on 15 March 1999.
Fourth launch
Four satellites on a Soyuz-Ikar from Baikonur on Thursday 10 February 1999.
That brought them to twelve satellites in orbit after losing twelve on the Zenit - a new
definition of break-even. Here's Wired News reporting.
Third launch (attempt and failure)
Globalstar lost twelve satellites
on a Russian Zenit 2 rocket launched on Wednesday, 9 September 1998, apparently
due to flight
control computer problems. The
launch was initially described as going well - apparently the announcer was
reading from a preplanned script and Globalstar employees didn't learn of the failure for
at least two hours.
The official website streamed the launch, but then removed the RealPlayer files in an attempt at spin control.
Apparently Globalstar expects to begin service in some latitudes
with only 32 satellites
active - this is one of the benefits of the diversity approach using CDMA
gives them. (Wired News, 10 September 1998)
Map showing trajectory of the failed launch from the BBC.
(That gave the people in the financial forums something to
chew over... they've been saying some silly things.)
Second launch
The second set of Globalstar satellites launched in April 1998.
First launch
The first Globalstar satellites were ready to launch in December 1997. That
first launch was rescheduled for 6 February 1998,
but strong winds delayed launch until 14th February.
Delays
and glitches hamper the launch (Wired News, 6 February 1998)
Gateways
Description of gateways from a networking
perspective.
Various
Technical summary from the Big LEO tables.
Description of Globalstar from the Small Satellites Home Page.
Globalstar operations centre.
Summary of Globalstar from
Computer Review.
Introduction to Globalstar from Alcatel.
Globalstar uses
CDMA communications technology from
Qualcomm. Here's their introduction to Globalstar.
Is CDMA that good? Some people have their doubts, more doubts, and proven doubts. And they've been
debating the
benefits of CDMA ever since.
Satellite production includes
Alenia Aerospazio.
Satellite phones from Ericsson.
Sun
sensors from EDO Corporation.
Discussion of Globalstar subsystems
from Paul Pomes.
Every circle in the cylindrical projection below is the coverage area, or
footprint, of a Globalstar satellite flying overhead at the centre
of the circle and looking down for signals. All but the highest latitudes
are completely covered.
48 operational satellites provide this coverage - the full constellation
as originally planned.
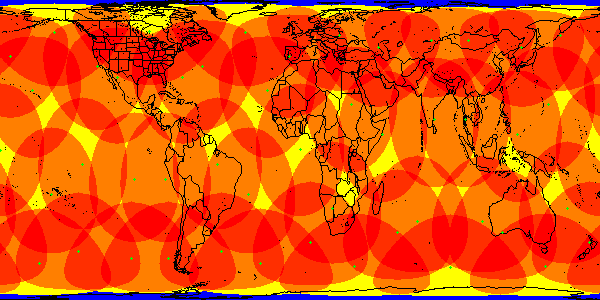
Globalstar's satellite footprints at a moment in time, generated by SaVi
The footprints move over the earth. There is no orbital seam.
Coverage requires a terrestrial gateway in or near a footprint.
cylindrical projection
Without sufficient gateways, coverage is sparse, as shown by
Globalstar USA's coverage map.
The financial market is going to determine all of this. At some point, we may exhaust the opportunity associated with satellite communications.
- Doug Dwyre.
Lloyd Wood
(L.Wood@society.surrey.ac.uk)
this page last updated 22 October 2010



